“Discover the Power of the Glycemic Index: Unlock Your Health Potential!”
Overview
Knowing the Glycemic Index (GI) of foods can help you make healthier food choices and better manage your blood sugar levels.
GI is a measure of how quickly a food containing carbohydrates raises your blood sugar levels. It is a numerical system of ranking foods based on their immediate effect on blood sugar levels.
What is the Glycemic Index and How Can it Help You Manage Your Blood Sugar?
Glycemic Index (GI) is a numerical system used to measure the effect of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. It is based on the concept that different carbohydrates have different effects on blood sugar levels.
The GI is a useful tool for people with diabetes, as it can help them to manage their blood sugar levels. Choosing foods with a low GI can help to keep their blood sugar levels stable. Eating a diet that is low in GI can also help to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
By using the GI, people with diabetes can make informed decisions about the types of carbohydrates they eat. This can help them to better manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing diabetes-related complications.
How to Use the Glycemic Index to Choose Healthy Foods
The glycemic index (GI) is a tool that ranks carbohydrates on a scale from 0 to 100, based on how quickly they are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream.
Foods with a high GI are quickly digested and absorbed, causing a rapid rise in blood sugar levels.
Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
To use the glycemic index to choose healthy foods, understand the GI ratings of different foods.
- Foods with a GI rating of 55 or less are considered low-GI foods
- Foods with a GI rating of 56 to 69 are considered medium GI foods
- Foods with a GI rating of 70 or higher are considered high-GI foods
Low GI foods are generally healthier than high GI foods, as they are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
When choosing foods, look for foods with a low GI rating like whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
Eating too many high GI foods can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, which can be damaging to health.
Glycemic Load and Its Impact on Blood Sugar
 The glycemic load (GL) is a measure of the impact of food on blood sugar levels. It is calculated as:
The glycemic load (GL) is a measure of the impact of food on blood sugar levels. It is calculated as:
GL=(Glycemic index of food x the number of carbohydrates it contains)/100
The GI is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels, while the GL is a measure of the overall effect of the food on blood sugar levels.
The GL of food can range from 0 to 20 or more.
- Foods with a GL of 0 do not affect blood sugar levels
- Foods with a GL of 20 or more can cause a significant spike in blood sugar levels.
Foods with a GL of 10 or less are considered to have a low glycemic load, while foods with a GL of 11-19 are considered to have a medium glycemic load.
The GL of a food is important to consider when planning meals, as it can help to regulate blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GL can be eaten more frequently, while foods with a high GL should be eaten in moderation.
Choose foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber. Eating a balanced diet that is low in GL and carbohydrates can help to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Eating Low Glycemic Index Foods
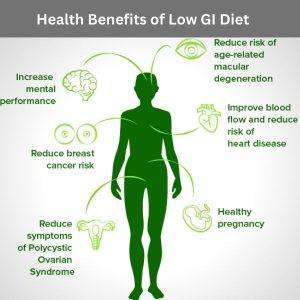 Eating low GI foods has been linked to numerous health benefits, including
Eating low GI foods has been linked to numerous health benefits, including
- Improved blood sugar control
- Reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
- Improved heart health
Low GI foods are typically high in fiber, which helps to slow down digestion and the release of sugar into the bloodstream. This helps to keep blood sugar levels stable and prevents spikes in insulin levels.
Eating low GI foods can also help to reduce hunger and cravings, as they are digested more slowly and provide a steady supply of energy.
Low GI foods can also help to reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases. Studies have shown that eating a diet rich in low GI foods can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
Low GI foods are also beneficial for weight management, as they help to keep you feeling fuller for longer and can reduce the risk of overeating.
Food Under Low Glycemic Index
Low glycemic index (GI) foods are those that are digested and absorbed slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. These foods are typically high in fiber, protein, and/or fat, which help to slow down digestion and absorption.  Examples of low GI foods include
Examples of low GI foods include
- whole grains– oats, barley, and quinoa are excellent sources of fiber and protein
- legumes– lentils, beans, and chickpeas are also high in fiber and protein
- fruits– apples, oranges, pomegranates, and berries are high in fiber and antioxidants
- vegetables– broccoli, spinach, and kale are high in fiber and vitamins
- nuts– almonds, walnuts
- seeds– flaxseeds are high in healthy fats and protein
Food Under High Glycemic Index
High glycemic index (GI) foods are those that cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. These foods are typically high in carbohydrates and have a GI value of 70 or higher.  Examples of high GI foods include
Examples of high GI foods include
- white bread
- white rice
- potatoes
- cornflakes
- pretzels
- most breakfast cereals
Other high GI foods include sugary snacks such as candy, cakes, and cookies.
Fruits such as watermelon, pineapple, and mangoes also have a high GI value.
Relationship Between Glycemic Index and Weight Loss
It is widely accepted that a low GI diet can help with weight loss, as it helps to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce hunger.
This study aims to investigate the relationship between GI and weight loss. To do this, a systematic review of the literature was conducted. Studies were included if they reported on the effects of GI on weight loss in adults. A total of 18 studies were included in the review.
The results of the review showed that a low GI diet was associated with greater weight loss than a high GI diet. This was true for both short-term and long-term weight loss.
The studies also showed that a low GI diet was associated with improved glycemic control and reduced hunger.
Overall, the results of this review suggest that a low GI diet may be beneficial for weight loss. However, further research is needed to confirm these findings and to explore the exact mechanisms by which GI affects weight loss.