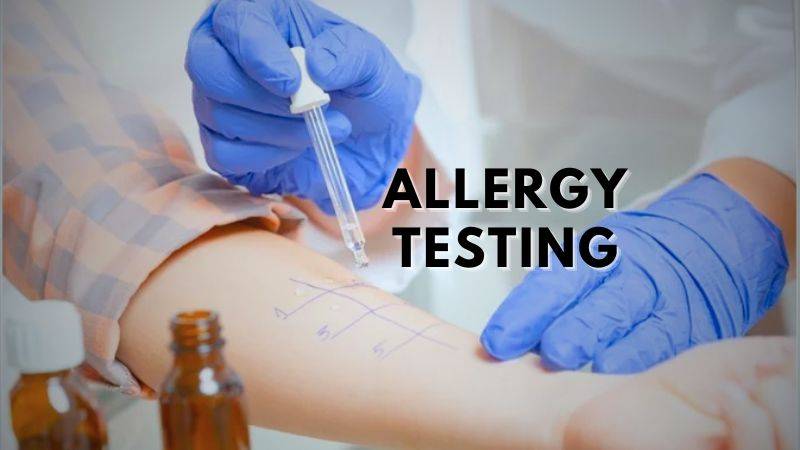
Allergy testing is a way doctors find out if your body reacts badly to certain things, called allergens. If you get an allergic reaction, it means you are allergic to something.
You might be allergic to stuff around you like mold, pollen from plants, or pet hair. Some people react badly when stung by a bee or when they touch latex. Others can’t eat certain foods like peanuts, milk, or soy because it makes them sick. This is also an allergy.
Let’s delve into the depth what are reasons and how to get rid of allergy!
Types of Allergens

Allergens are things that can cause an allergic reaction. There are mainly three kinds of allergens:
- Inhaled allergens: These are things you breathe in that can cause an allergy. Pollen is a common one.
- Ingested allergens: These are things you eat that can cause an allergy. Foods like peanuts, soy, and seafood are examples.
- Contact allergens: These are things that cause an allergic reaction when they touch your skin. Poison ivy, for example, can cause a rash and itching.
An allergy test is when doctors expose you to a tiny amount of an allergen to see if you react to it.
Why do Doctors perform Allergy Tests?

Doctors might do an allergy test if you have allergy symptoms that are bothering you. They also do these tests for people with asthma, as it can help figure out what things might make their asthma worse or cause an asthma attack.
If you’ve had a really bad allergic reaction called anaphylaxis, you might also need an allergy test.
Anaphylaxis is dangerous and can cause things like hives or swelling, trouble breathing, and a big drop in blood pressure that can lead to shock.
By looking at your health history and doing allergy testing, doctors can figure out what caused the severe reaction.
Need for Allergy Testing
If you’re allergic to things in the air like dust, pollen, or pet fur, you could get allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever. This allergy could cause:
- Headaches.
- Itchy or watery eyes.
- Blocked nose, sneezing, or runny nose.
- Difficulty breathing, wheezing, or constant cough.
- Sore throat.
Food allergy symptoms usually show up within 30 minutes to two hours after you eat. If you’re allergic to certain foods, you might have:
- Skin reactions like hives, swollen face, lips or tongue, or itchy skin.
- Breathing problems like coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, or feeling a tightness in your chest or throat.
- Stomach and intestine problems like feeling sick and throwing up, belly pain and cramps, or diarrhea.
- Heart and blood symptoms like pale skin, weak pulse, or feeling dizzy or light-headed.
Some people are allergic to latex, certain smells, or metals like nickel, which can cause contact dermatitis, a skin reaction. If you have this kind of allergy, you might:
- Feel a burning sensation on your skin or get blisters.
- Have hives and swelling.
- Get a skin rash or itchy skin.
A skin test called a patch test can be done by a skin doctor (dermatologist) to figure out if you have these kinds of reactions.
Different Methods for Allergy Testing

There are several ways doctors can test for allergies. The best method for you will depend on your symptoms and what you might be allergic to.
Here’s a look at the different tests:
Skin prick (scratch) test: In this test, your doctor uses a thin needle to prick your skin with different things that might cause allergies. They might also put small drops of these substances on your skin and use a device to scratch the skin slightly. If you’re allergic, your skin will get red within about 15 minutes. You might get a rash or raised, round spots called wheals. This test is used for checking allergies to things in the air, food allergies, and allergies to penicillin.
Intradermal skin test: If the skin prick test doesn’t give clear results, your doctor might do an intradermal skin test. In this test, the doctor injects a small amount of the allergen into the top layer of your skin. This test can check for allergies to airborne irritants, medicines, and insect stings.
Patch test: If you have contact dermatitis, a patch test can help figure out what’s causing it. Your doctor puts a drop of an allergen on your skin and covers it with a bandage, or they might use a patch that has the allergen on it. You keep the bandage on for 48 to 96 hours, and then your doctor checks your skin for a rash or other reaction.
Blood (IgE) test: In this test, your doctor sends a sample of your blood to a lab. The lab adds allergens to the blood and measures the amount of IgE antibodies in it. This test can sometimes give false-positive results.
Challenge tests: In a challenge test, you swallow a small amount of an allergen while a doctor watches you closely. This test is usually done by an allergist, a doctor who specializes in allergies. This test needs to be done under close medical supervision because it can cause a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. If you have anaphylaxis, the doctor can give you an injection of a medicine called epinephrine to stop the reaction.
Are there any risks to getting an allergy test?
The main risk of an allergy test is having a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. This is not common, but it can happen.
Doctors are always ready for this and have a medicine called epinephrine on hand. They can give you emergency treatment if you have a severe reaction during the test.
Allergy Test Results
The results of an allergy test can be:
Negative: This means you’re not allergic to the substance. It’s very rare to get a wrong negative result (this is when the test says you don’t have an allergy but you actually do).
Positive: This means you’re allergic to the substance. However, even if the test shows you’re allergic, you might not always have a reaction to the allergen. There’s also a chance you could get a false positive result, especially from a blood (IgE) test. This is when the test says you’re allergic but you’re actually not.
Living with Allergies: Steps to Manage Your Allergic Reactions
If you have an allergy, your doctor might suggest one or more of these things:
Avoid allergens: Try to stay away from things that cause serious reactions, like latex or certain foods.
Take allergy medicine every day: Antihistamines can help prevent or lessen symptoms of allergic rhinitis and other allergy symptoms.
Get allergy shots: These shots, also called immunotherapy, can help your immune system react less to certain allergens like pet dander. You usually need to get these shots for three to five years to get the most benefit. They can be expensive, but often provide long-lasting relief even after you stop getting the shots.
Have a medical alert card or jewelry: This lets other people know about your severe allergy. It tells them that you could have a serious allergic reaction called anaphylaxis to things like peanuts or bee stings.
Carry an epinephrine injector (EpiPen): If there’s a chance you could have an anaphylactic reaction, you should always have this medicine with you.
Take Care of Yourself!
Also Read