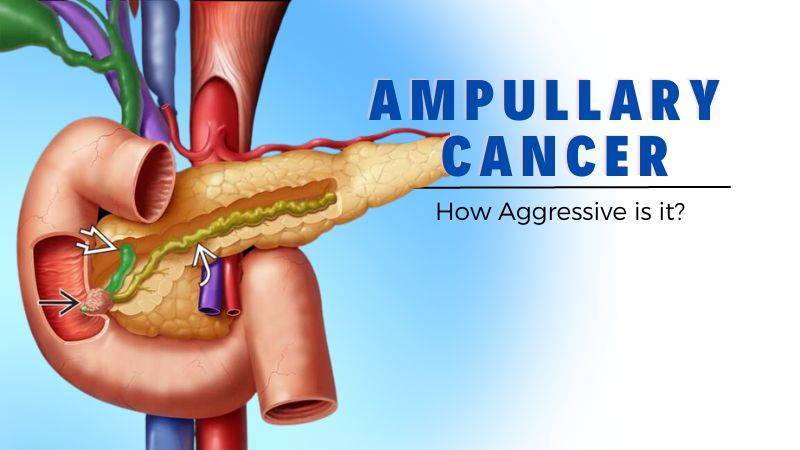
” Targeting Cancer, Saving Lives.”
Radiation therapy is a type of cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells.
It is a safe and effective treatment for many types of cancer and can be used to treat both early-stage and advanced cancers.
Different Types
There are several different types of radiation therapy, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) is the most common type of radiation therapy. It is delivered from a machine outside the body and is used to treat tumors in the chest, abdomen, pelvis, head, and neck. EBRT is typically given in multiple treatments over several weeks.
- Brachytherapy is a type of therapy that is delivered from inside the body. It is used to treat tumors in the prostate, cervix, and other areas. Brachytherapy involves placing radioactive material directly into the tumor or near the tumor. The radiation is then released over some time, usually a few days or weeks.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is used to treat tumors in the brain and spine. It is delivered from a machine outside the body and is used to deliver a single, high dose of radiation to the tumor. SRS is typically used to treat tumors that are too small or too deep to be treated with traditional radiation therapy.
- Intraoperative radiation therapy (IORT) is delivered during surgery. It is used to treat tumors in the breast, prostate, and other areas. IORT is typically used to treat tumors that are too small or too deep to be treated with traditional radiation therapy.
- Proton beam therapy uses protons instead of x-rays to treat tumors. It is used to treat tumors in the brain, spine, and other areas. Proton beam therapy is typically used to treat tumors that are too small or too deep to be treated with traditional radiation therapy.
 Benefits for Cancer Treatment
Benefits for Cancer Treatment
This therapy is a common and effective treatment for cancer. It is used to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors, and can be used alone or in combination with other treatments such as chemotherapy and surgery.
It is a non-invasive treatment that can be used to treat cancer without the need for surgery.
It is also highly targeted, meaning that it can be used to treat specific areas of the body without damaging healthy tissue. This makes it an ideal treatment for cancers that are located in hard-to-reach areas, such as the brain or spine.
This therapy can also be used to reduce the size of tumors before surgery, making it easier for surgeons to remove them. It can also be used to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence after surgery.
Latest Advances in Technology
Radiation therapy is a powerful tool in the fight against cancer, and the technology behind it is constantly evolving. The latest advances in radiation therapy technology are making it easier and more effective than ever before to treat cancer.
One of the most exciting advances in technology is the use of intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT). IMRT is a type of radiation therapy that uses computer-controlled x-ray beams to deliver precise doses of radiation to the tumor.
This allows for more accurate targeting of the tumor, reducing the risk of damage to healthy tissue. IMRT also allows for higher doses of radiation to be delivered, which can be more effective in treating certain types of cancer.
Another advancement in technology is the use of image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT). IGRT uses imaging techniques such as CT scans and MRI scans to create a 3D map of the tumor and surrounding tissue. This allows the radiation oncologist to precisely target the tumor and reduce the risk of damage to healthy tissue.
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is another type of radiation therapy that is becoming increasingly popular. SBRT uses high doses of radiation to target tumors with extreme precision. This allows for fewer treatments and shorter treatment times, making it a more convenient option for many patients.
Side Effects & Preventions
Radiation therapy can cause skin irritation in the area being treated. This can range from mild redness and itching to more severe blistering and peeling. To reduce skin irritation, patients should keep the area clean and dry and use moisturizers as recommended by their doctor.
It can also cause fatigue. This is due to the body’s response to the radiation, and it can last for several weeks after treatment. To help manage fatigue, patients should get plenty of rest and exercise regularly.
It can also cause nausea and vomiting. This is usually mild and can be managed with medications prescribed by the doctor.
This therapy can also cause changes in the taste of food. This can make eating difficult, but it is usually temporary and will improve over time.
The therapy can also cause changes in the hair in the area being treated. This can range from thinning to complete hair loss. Hair usually grows back after treatment, but it may be a different color or texture.
To understand the potential side effects of therapy before beginning treatment patients should talk to their doctor about any concerns they have and follow their doctor’s instructions for managing side effects.
Let us watch how is Radiation Treatment given


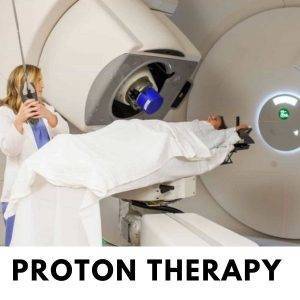 Benefits for Cancer Treatment
Benefits for Cancer Treatment