What is Anemia | RBC Functions | Causes | Symptoms | Types | Effects of Being Anemic | Diagnosis | Treatment | Self Care Ways | Conclusion |
Anemia-a medical condition that affects millions of people around the world, making it one of the most common blood disorders.
This condition occurs when the number of red blood cells (RBCs) or the amount of hemoglobin (a protein that carries oxygen) in the body is lower than normal.
This reduction can interfere with the blood’s ability to deliver oxygen to tissues and organs, which can cause a variety of health issues.
What is Anemia?
Anemia is a decrease in the quantity of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood.
Hemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
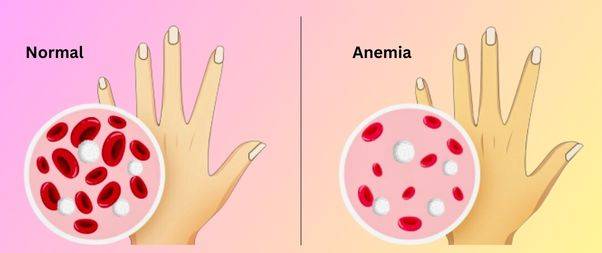
When you’re anemic, your body isn’t receiving the amount of oxygen it needs to function properly, which can lead to fatigue and other symptoms.
Anemia can be temporary or long term, and its severity can range from mild to severe.
It can also be a warning sign of serious illnesses, such as cancer or kidney disease.
It’s crucial to get anemia diagnosed promptly and treated effectively.
What Red Blood Cells Do?

Your body makes three types of blood cells.
- White blood cells help fight off germs
- Platelets help your blood to stick together and form clots
- Red blood cells carry oxygen all over your body.
Red blood cells contain a protein full of iron that makes blood red, and this is called hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin helps red blood cells move oxygen from your lungs to everywhere else in your body. It also helps move carbon dioxide from different parts of your body to your lungs, so you can breathe it out.
The soft, spongy part inside many of your big bones, known as bone marrow, makes red blood cells and hemoglobin.
To make these, your body needs iron, vitamin B-12, folate, and other nutrients from the food you eat.
Causes of Anemia
Anemia can be caused by several factors, including:
- Iron deficiency: This is the most common cause of anemia. The body requires iron to produce hemoglobin. Iron deficiency can occur due to a diet low in iron, poor absorption of iron by the body, or blood loss from menstruation or injury.
- Vitamin deficiency: Besides iron, the body also needs vitamin B12 and folic acid to produce enough healthy red blood cells. A diet lacking in these and other key nutrients can cause decreased red blood cell production.
- Chronic diseases: Certain diseases, such as cancer, HIV/AIDS, rheumatoid arthritis, kidney disease, and other inflammatory diseases, can interfere with the production of red blood cells, resulting in chronic anemia.
- Inherited and hemolytic anemias: Some anemias, like sickle cell anemia and thalassemia, are inherited. Hemolytic anemias occur when the body destroys red blood cells faster than it can produce them.
Symptoms
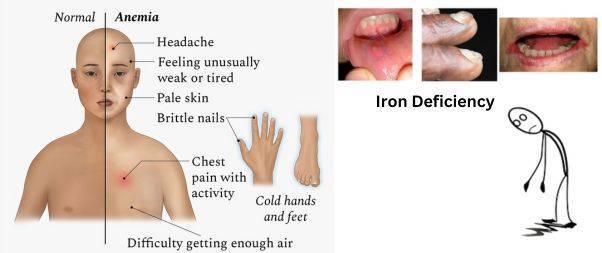
If you have anemia, you might feel really tired and find it hard to do your usual activities. You could also notice other changes like:
- Feeling out of breath, even when you’re not doing much.
- Feeling dizzy or wobbly when you stand or move around.
- Your heartbeat might feel fast, uneven, or like it’s skipping a beat.
- You might hear a swooshing noise in your ear from time to time.
- You could get headaches more often.
- Your skin might look paler or more yellow than it usually does.
- You might feel a squeezing or pressing pain in your chest.
Types of Anemia
Anemia comes in many forms and happens when the levels of red blood cells in your body are low. Here’s a breakdown:
Anemias related to nutrition
- Pernicious anemia: This is when your body can’t absorb vitamin B12, leading to anemia.
- Iron-deficiency anemia: This happens when your body lacks iron, which it needs to make hemoglobin, a protein that helps red blood cells carry oxygen.
- Megaloblastic anemia: This type of anemia happens when you’re low in vitamin B12 and/or vitamin B9 (folate).
Anemias that you can inherit
- Sickle cell anemia: This changes the shape of your red blood cells into stiff, sticky cells that can block blood flow.
- Fanconi anemia: This is a rare disorder that can lead to anemia.
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia: This condition stops your bone marrow from making enough red blood cells.
Anemias caused by abnormal red blood cells
- Hemolytic anemia: This type of anemia happens when your red blood cells break down or die faster than usual.
- Aplastic anemia: This is when the stem cells in your bone marrow don’t make enough red blood cells.
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: This happens when your immune system attacks your red blood cells.
- Sideroblastic anemia: This is when you don’t have enough red blood cells and too much iron in your system.
- Macrocytic anemia: This is when your bone marrow makes red blood cells that are unusually large.
- Microcytic anemia: This happens when your red blood cells are smaller than usual because they don’t have enough hemoglobin.
- Normocytic anemia: This type of anemia means you have fewer red blood cells than usual, and they don’t have the normal amount of hemoglobin.
Effects of Being Anemic
When you have anemia, it means you’re showing symptoms like feeling really tired or always being cold.
Anemia affects people in different ways:
Babies: Some babies are born with a low number of red blood cells. Most of these babies won’t need treatment for anemia, but those with severe anemia might need a blood transfusion.
Infants: Babies might not get enough iron when they start eating solid food. This is because solid food doesn’t give them iron as easily as breast milk or formula does. Babies with anemia might seem really tired.
Kids: Kids grow a lot from the time they’re born until they’re 2 years old. Kids who are growing quickly need more iron. If a child has anemia, they might develop problems like slower development of motor skills and learning difficulties.
Pregnant women: Pregnant women might get iron-deficiency anemia, which can increase the chance of problems like giving birth early or having a baby with low birth weight.
Women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB): Women and AFAB individuals with heavy periods or conditions like uterine fibroids might lose a lot of blood and get anemia.
People who are 65 and older: Older people are more likely to eat diets low in iron and have certain long-term illnesses that make them more likely to get anemia. If they do get anemia, they might develop heart problems or weakness that makes it hard for them to move around. They might also feel confused or depressed.
People with long-term illnesses: Some long-term illnesses like autoimmune diseases or cancer can make you more likely to get anemia.
Anemia is actually pretty common. It’s thought to affect about one-third of all the people in the world and around 3 million people in the United States.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will ask about how you’re feeling to help diagnose anemia. Since anemia means you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells, they will also do some blood tests:
- Complete blood count (CBC): This is a test where doctors check all your blood cells, especially the red ones. They look at how many red blood cells you have, their size, and their shape. They might also use this test to see how much vitamin B12 or B9 you have in your body.
- Peripheral blood smear: In this test, doctors look at your red blood cells under a microscope.
Treating Anemia
Treatment of anemia varies greatly and depends on the cause, severity, and type of anemia.
- In some cases, dietary changes or supplements can help, such as increasing the intake of iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid.
- For iron deficiency anemia, doctors often recommend iron supplements along with a diet rich in iron.
- If the cause of anemia is a chronic disease, the focus will be on managing the underlying disease.
- In severe cases, medical procedures such as blood transfusions or a bone marrow transplant may be necessary.
- Inherited forms of anemia like thalassemia or sickle cell anemia may require lifelong treatment and management.
Self-Care Strategies for Managing Anemia
While some kinds of anemia are short-lived and mild, others can last your whole life.
Here are some ways you can manage anemia:
- Eat a healthy diet: One of the main reasons people get anemia is because of a poor diet. Talk to your doctor about foods that are high in iron and other foods you should be eating.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Exercise regularly: Before you start, ask your doctor about safe ways to exercise.
- Avoid contact with certain chemicals: Being around certain metals can cause a type of anemia where your red blood cells break down too fast.
- Wash your hands often to avoid getting sick: You might also want to ask your doctor about vaccines that can protect you against common infections.
- Take care of your teeth and visit the dentist regularly: If you have iron-deficiency anemia, you might have problems with your teeth.
- Keep an eye on your symptoms and tell your doctor if anything changes.
Conclusion
Anemia is a common but potentially serious condition. If you suspect you have anemia due to persistent fatigue or other symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
While some forms of anemia cannot be prevented, living a healthy lifestyle often helps prevent many types of anemia or keep them from becoming severe.
Remember, understanding anemia and recognizing its symptoms is the first step towards effective treatment.
With prompt diagnosis and the correct treatment, most people with anemia can expect to lead a normal, healthy life.
Take care of Yourself!
Also Read






